Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit trusted apps and browser extensions.
Since people tend to trust tools that seem legitimate, attackers use them to spread malware or steal sensitive data. A new report reveals that over 3.2 million users have been affected by a security breach involving malicious browser extensions.
These extensions, which appeared genuine, were secretly embedding harmful scripts, stealing data and manipulating search results.
A man using a Chrome browser. (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
How were the extensions compromised?
GitLab Security has uncovered a major security breach affecting over 3.2 million users through a network of compromised browser extensions, including some linked to GitLab. The attack stemmed from a supply chain breach, where threat actors infiltrated legitimate extensions and pushed malicious updates. These updates embedded hidden scripts that allowed unauthorized data collection, altered HTTP requests and injected ads into web pages, all without users noticing.
Originally built for tasks like ad blocking, emoji input and screen recording, these extensions were repurposed through covert updates that exploited the extensive permissions users had granted, enabling real-time manipulation of web activity.
Typically, malicious extensions or apps are created solely to steal data, with their advertised functionality being an afterthought or simply a way to get listed in an official store. That was not the case here. These were legitimate extensions that became harmful only after attackers injected malicious updates into them.

An illustration of a hacker at work (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
THE HIDDEN COSTS OF FREE APPS: YOUR PERSONAL INFORMATION
Which extensions are affected?
Several of the compromised extensions are commonly utilized and may be present in your browser. For instance, ad blockers such as AdBlock are valued for eliminating disruptive advertisements and enhancing browsing privacy. However, in this breach, these tools were manipulated to deliver malicious payloads. The following extensions have been identified as affected:
- Blipshot: Takes full-page screenshots with one click
- Emojis – Emoji Keyboard: Provides an emoji keyboard for easy access
- WAToolkit: A toolkit for WhatsApp Web
- Color Changer for YouTube: Allows customization of YouTube’s color scheme
- Video Effects for YouTube And Audio Enhancer: Adds effects and enhances audio for YouTube videos
- Themes for Chrome and YouTube™ Picture in Picture: Offers themes and picture-in-picture functionality
- Mike Adblock für Chrome: A German ad blocker for Chrome
- Page Refresh: Automatically refreshes web pages
- Wistia Video Downloader: Enables downloading of Wistia videos
- Super dark mode: Provides a dark theme for websites
- Emoji keyboard emojis for Chrome: Another emoji keyboard for Chrome
- Adblocker for Chrome – NoAds: Blocks ads while browsing
- Adblock for You: Another ad-blocking extension
- Adblock for Chrome: Yet another ad blocker for Chrome
- Nimble capture: A tool for capturing web content
- KProxy: A proxy service for anonymous browsing
If any of these extensions are installed on your browser, it is recommended that you assess their permissions and consider their removal until official security updates are verified.
The malicious extensions bypassed Content Security Policy protections, which are designed to prevent cross-site scripting attacks, allowing attackers to modify web content without detection. They also communicated with command-and-control servers to receive further instructions, showing a high level of coordination. The attackers exploited the trust users place in the Chrome Web Store and its automatic update system. Investigations suggest this activity has been ongoing since at least July 2024.
Clarification on affected extensions
Some of the compromised extensions listed above have generic names that may resemble well-known and legitimate tools, but they are not the same. For example, “Password Manager” in our list refers to a malicious extension identified in the breach, not to reputable password manager services we mention here. Similarly, extensions named “AdBlock Plus” or “VPN Extension” in this context are not necessarily the widely trusted versions but rather imitations or malicious variants.
To ensure you’re using a legitimate extension, follow these steps.
- Verify the developer – Always check the extension’s publisher in the Chrome Web Store or Firefox Add-ons. Official brands like Norton, Google or Microsoft will be clearly listed.
- Check the reviews and downloads – Malicious extensions often have lower ratings, generic reviews or a small number of downloads compared to their legitimate counterparts.
- Avoid third-party sites – Only install browser extensions directly from trusted sources like the Chrome Web Store, Mozilla Add-ons or the official website of the developer.
- Monitor for unusual behavior – If an extension starts requesting excessive permissions or behaving differently than expected (e.g., injecting ads, slowing down browsing), it could be compromised.

Google Chrome on a smartphone (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
FROM TIKTOK TO TROUBLE: HOW YOUR ONLINE DATA CAN BE WEAPONIZED AGAINST YOU
How to remove an extension from Google Chrome
If you have installed one of the above-mentioned extensions on your browser, remove it as soon as possible. To remove an extension from Google Chrome, follow these steps.
- Open Chrome and click the icon that looks like a piece of a puzzle. You’ll find it in the top-right corner of the browser.
- You can see all the active extensions now. Click the three dots icon next to the extension you want to remove and select Remove from Chrome.
- Click Remove to confirm.
WHAT IS ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)?
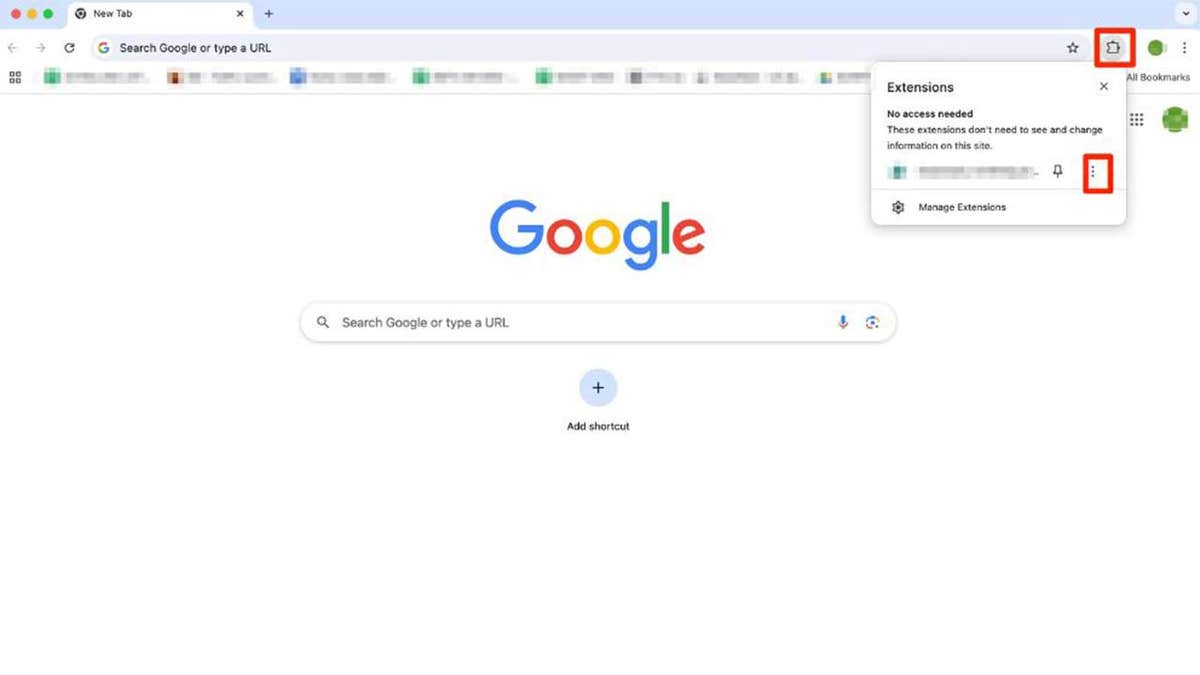
Steps to remove an extension from Google Chrome (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
6 ways you can protect your personal data
Here are 6 ways to safeguard your sensitive information and maintain your online privacy:
1. Keep your browser and extensions up to date: Outdated software is a goldmine for cybercriminals. Bugs or security gaps in old versions of your browser or extensions can be exploited to inject malicious code, steal data or take control of your system. Updates patch these vulnerabilities, making them a critical line of defense. Turn on automatic updates for your browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge) so you’re always running the latest version without thinking about it. See my guide on keeping your devices and apps updated for more information.
2. Install extensions only from trusted sources: Official browser stores like the Chrome Web Store or Firefox Add-ons have rules and scans to catch bad actors, but they’re not perfect. Extensions from random websites or third-party downloads are far more likely to hide malware or spyware. Stick to the official store for your browser. Don’t download extensions from sketchy links.
3. Have strong antivirus software: The best way to safeguard yourself from malicious links that install malware, potentially accessing your private information, is to have antivirus software installed on all your devices. This protection can also alert you to phishing emails and ransomware scams, keeping your personal information and digital assets safe. Get my picks for the best 2025 antivirus protection winners for your Windows, Mac, Android and iOS devices.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
4. Be skeptical of extensions requesting unnecessary access: Some extensions overreach on purpose. A calculator tool asking for your browsing history or a weather app wanting your login data is a huge red flag.
Before installing, ask, “Does this permission match the extension’s job?” If the answer is no, don’t install it. Watch out for broad permissions like “Read and change all your data on websites you visit” unless it’s clearly justified (e.g., a password manager). If an update suddenly adds new permission requests, dig into why. It might mean the extension has been sold or hacked.
5. Update your passwords: Change passwords for any accounts that may have been affected by the incident, and use unique, strong passwords for each account. Consider using a password manager. This can help you generate and store strong, unique passwords for all your accounts. Get more details about my best expert-reviewed Password Managers of 2025 here.
6. Remove your personal data from public databases: If your personal data was exposed in this security incident, it’s crucial to act quickly to reduce your risk of identity theft and scams. While no service can guarantee the complete removal of your data from the internet, a data removal service is really a smart choice. They aren’t cheap and neither is your privacy. These services do all the work for you by actively monitoring and systematically erasing your personal information from hundreds of websites. It’s what gives me peace of mind and has proven to be the most effective way to erase your personal data from the internet. By limiting the information available, you reduce the risk of scammers cross-referencing data from breaches with information they might find on the dark web, making it harder for them to target you. Check out my top picks for data removal services here.
MASSIVE SECURITY FLAW PUTS MOST POPULAR BROWSERS AT RISK ON MAC
Kurt’s key takeaways
Browser extensions can improve functionality but also pose significant security risks if not carefully managed. If you have any of the above extensions installed in Chrome, you should remove them immediately. Treat your browser as a key part of your digital security. Regularly check your extensions, remove unnecessary permissions and be cautious about automatic updates, even from trusted sources.
Should browsers implement stricter restrictions on what extensions can do by default? Let us know by writing us at Cyberguy.com/Contact.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
For more of my tech tips and security alerts, subscribe to my free CyberGuy Report Newsletter by heading to Cyberguy.com/Newsletter.
Ask Kurt a question or let us know what stories you’d like us to cover.
Follow Kurt on his social channels:
Answers to the most-asked CyberGuy questions:
New from Kurt:
Copyright 2025 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.



